Understanding Ethereum Mining
Ethereum mining is a cornerstone activity within the blockchain world that not only contributes to the creation of new Ether but also ensures the security and functionality of the Ethereum network.
What is Ethereum Mining?
Ethereum mining is the process by which new transactions are verified and added to the Ethereum blockchain. This computational process involves miners using specialized hardware, such as Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), to solve complex mathematical problems or puzzles. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add a new block to the blockchain and, as a reward, receives Ether tokens. This process operates on a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which is similar to that of Bitcoin.
However, it is important to note that as of September 2022, Ethereum has transitioned from PoW to a proof-of-stake (PoS) model. This shift aims to make the network more secure, sustainable, and scalable, which has significant implications for mining activities.
Importance of Ethereum Mining
Prior to the transition to PoS, mining played a pivotal role in Ethereum’s ecosystem. It was essential for the creation of new Ether, which incentivized miners to contribute their computational power to the network. Additionally, mining helped secure the network by making it computationally difficult for a single entity to manipulate the blockchain.
Mining also facilitated the processing and confirmation of transactions, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the Ethereum network. Miners were rewarded for their efforts in the form of Gas fees, transaction fees, and block rewards, which provided a financial incentive to support the blockchain’s infrastructure.
Despite the recent changes, understanding the history and function of Ethereum mining remains important for those interested in the cryptocurrency and blockchain space. For those looking to engage with Ethereum post-mining era, exploring options such as staking might be of interest. To learn more about the benefits of staking Ethereum, visit should-i-stake-my-ethereum.
The shift to PoS does not diminish the legacy of Ethereum mining; rather, it marks a new chapter of growth and development for the network, aligning with broader trends towards sustainability and efficiency in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Ways to Mine Ethereum
Ethereum mining can be an engaging way to participate in the Ethereum network and potentially earn rewards. There are three primary methods to mine Ethereum: Pool Mining, Solo Mining, and Cloud Mining. Each method has its own set of advantages and drawbacks, and the choice depends on one’s resources, expertise, and investment willingness.
Pool Mining
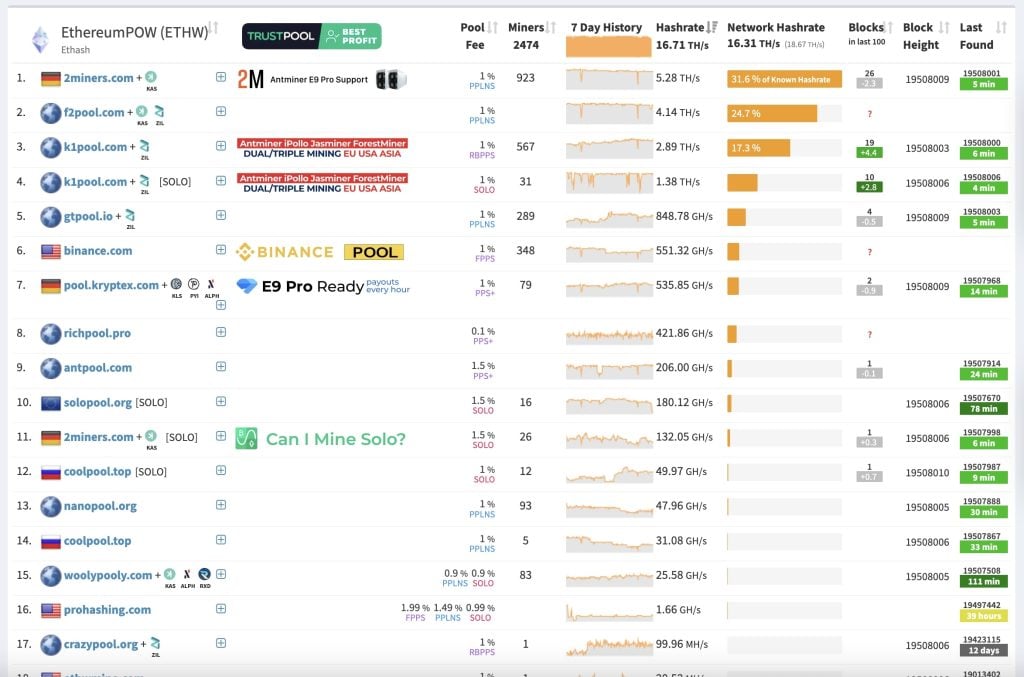
Pool mining is a popular method of mining where multiple miners combine their computational power to increase their chances of successfully mining a block. When a block is mined, the reward is distributed among the pool participants in proportion to the amount of computational power contributed. This approach is advantageous for individual miners who may not have enough processing power to mine Ethereum on their own.
| Pool Mining Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Chances | By pooling resources, miners have a higher probability of finding blocks and receiving rewards. |
| Steady Payouts | Rewards are more frequent, though smaller, which can be preferable for consistent income. |
| Reduced Risk | The collective effort reduces the risk associated with the volatility of mining success. |
To participate in pool mining, miners need to join an existing mining pool and follow their specific protocols. It is important for miners to consider the pool size, fee structure, and payout frequency before joining. Detailed information on pool mining can be found in our guide to how-to-mine-litecoin.
Solo Mining
Solo mining is the process of mining Ethereum independently without joining a pool. This method allows miners to receive the entire reward for mining a block. However, the chances of successfully mining a block on one’s own are significantly lower compared to pool mining, especially for individuals with limited computational power.
| Solo Mining Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Rewards | Miners keep the entire reward, increasing potential profits if a block is mined. |
| Independence | Miners have complete control over their mining operations and decisions. |
| No Pool Fees | There are no fees to pay to a pool, maximizing potential earnings. |
Solo mining requires significant investment in hardware and electricity, and it involves a higher level of risk due to the competitive nature of mining. Those interested in the intricacies of solo mining can explore related topics, such as monero-mining-software.
Cloud Mining
Cloud mining is a method that allows individuals to participate in Ethereum mining without owning or managing any mining hardware. Instead, miners rent computing power from a cloud mining service provider. This option can be attractive for those who wish to mine Ethereum without the hassle of setting up and maintaining mining equipment.
| Cloud Mining Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Convenience | No need to purchase or maintain mining hardware. |
| Accessibility | Allows individuals to mine Ethereum who may not have the technical expertise or resources. |
| Predictable Costs | Fixed costs with cloud mining contracts can help in budgeting and cost analysis. |
While cloud mining offers convenience, it’s essential to conduct thorough research on the cloud mining provider’s reputation and the terms of the mining contract. Potential risks include fraud and lower profits due to operational costs and fees charged by the provider. For insights into the benefits and precautions of cloud mining, see our article on what-is-bome.
Each mining method presents unique opportunities and challenges for Ethereum enthusiasts. By weighing the factors such as initial investment, potential rewards, and risk tolerance, miners can select the most suitable approach to mine Ethereum. As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, it’s also important to stay informed about the future of Ethereum mining, including the anticipated transition to Proof of Stake and its implications for miners.
Factors to Consider in Ethereum Mining
For those looking to delve into the world of cryptocurrency mining, specifically Ethereum, there are several critical factors that must be taken into account to ensure profitability and efficiency. From choosing the right mining pool to understanding the costs involved, making informed decisions is key to a successful mining operation.
Pool Size and Rewards
When participating in pool mining for Ethereum, the size of the pool has a direct impact on the frequency of rewards. Larger pools may increase the chances of consistently finding blocks due to their collective hashing power. However, the rewards are distributed among more participants, which can result in smaller individual payouts. Conversely, smaller pools may offer larger individual rewards but with less frequency. It’s important to consider minimum payout thresholds and pool fees, with around a 1% fee being a common benchmark for reliability. Additionally, the number of blocks found can be influenced by the pool’s size, potentially affecting the miners’ rewards as more miners join the pool (Simplilearn).
| Pool Size | Frequency of Rewards | Individual Reward Size |
|---|---|---|
| Large | High | Smaller |
| Small | Low | Larger |
Resource Requirements
To gain profitability in Ethereum mining, a significant investment in hardware resources is required. For instance, to mine approximately $500 a month, a miner would need a hashrate of about 600MH/s. Achievable configurations could include setups such as 8 Radeon VIIs, 12 RX 5700 XTs, or 20 RX 580s. It’s crucial to consider not only the initial cost of building a mining rig with these components but also ongoing expenses such as electricity.
| Hardware Configuration | Estimated Hashrate (MH/s) |
|---|---|
| 8 Radeon VIIs | 600 |
| 12 RX 5700 XTs | 600 |
| 20 RX 580s | 600 |
Cost Analysis
The profitability of mining Ethereum is heavily influenced by the current price of Ethereum, the mining difficulty, and electricity rates. The substantial investment required for mining hardware and the cost of electricity are pivotal factors that can significantly impact the return on investment. In regions where electricity is more expensive, mining may quickly become unprofitable. Prospective miners should perform a thorough cost analysis, taking into account the electricity consumption of their mining setup and the local electricity rates to determine if Ethereum mining is a viable endeavor.
For those considering mining on a smaller scale, the profitability may be challenging unless they have access to substantial resources, such as over 100 graphics cards. Solo mining has become increasingly difficult due to competition with large networks of miners and companies (BitDegree.org).
To further explore the topic of Ethereum mining and related cryptocurrency ventures, be sure to read about what is Bome, Monero mining software, or the best staking crypto opportunities. Additionally, those considering the long-term commitment to Ethereum can find valuable insights in should I stake my Ethereum.
Ethereum Mining Process
The process of Ethereum mining is intricate and involves setting up a dedicated mining rig, installing the right mining software, and understanding the distribution of rewards. This section will guide those interested in the process of how to mine Ethereum, providing insights into the essential steps.
Setting Up Mining Rig
To embark on mining Ethereum, the first step is assembling a powerful computer system specifically designed for mining. This system, often referred to as a mining rig, typically requires one or more high-performance GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) cards or a dedicated ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miner like the Bitmain Antminer E9 for profitable mining operations. Here’s a basic checklist for setting up your mining rig:
- High-performance GPU or ASIC miner
- Cooling system to prevent overheating
- Reliable high-speed internet connection
- Location with low electricity costs for economic feasibility
The initial investment in a mining rig can be substantial, but it is a critical factor that determines the efficiency and success of your mining operations. It’s also advisable to ensure that your rig is in a location with low power costs and a stable internet connection to maximize profitability (ClearTax).
Mining Software
Once your mining rig is ready, the next step is to install necessary mining software. This software will connect you to the Ethereum blockchain and the network of miners. Popular Ethereum mining software includes:
- Geth
- PhoenixMiner
- Claymore Miner
Each software option has its own set of features and can impact the efficiency of your mining. It’s important to choose software that is compatible with your hardware and offers the best performance. The software will also help you join a mining pool if you choose not to mine solo and will keep track of your earnings.
Rewards Distribution
When you successfully mine Ethereum, you are rewarded with Ether tokens. In the context of pool mining, these rewards are divided among participants based on the hashing power each miner has contributed. Most pools distribute rewards at regular intervals, depending on the collective mining success of the group.
Ethereum miners currently receive approximately 3.5 ETH for adding a new block to the blockchain, with a new block being created every 14-16 seconds. The rewards are then transferred to the miner’s synced cryptocurrency wallet.
To better understand the distribution of rewards and the consensus mechanism, you may want to explore related topics such as should I stake my Ethereum or delve into the differences between various consensus algorithms with articles like what is BOME.
The process of mining Ethereum is a combination of hardware setup, software configuration, and strategic consideration of reward distribution. While the rewards can be significant, it’s crucial to stay informed about the changing landscape of Ethereum mining, including the potential shift from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, to make the most out of your mining endeavors.
Challenges and Risks in Ethereum Mining
While Ethereum mining can be a profitable venture, it’s not without its challenges and risks. Understanding these is crucial for anyone considering mining Ethereum. We’ll explore some of the common risks associated with pool mining, the cost considerations to keep in mind, and the security concerns inherent in the mining process.
Pool Mining Risks
In pool mining, miners combine their computational resources to increase their chances of successfully mining a block. However, this approach has several risks:
- Dishonest Pool Operators: Some pool operators might not distribute rewards fairly or could potentially abscond with the rewards altogether.
- Pool Shut Down: A pool might abruptly cease operations, possibly due to insolvency, leaving miners without their expected rewards.
- Security Breaches: Mining pools can be targets for hackers who may steal cryptocurrencies or disrupt mining operations.
- Centralization Risk: Larger pools can control significant portions of the network’s hash rate, posing risks of centralization.
One example of pool mining risks is the potential for a pool operator to fail to fairly distribute rewards or to shut down the pool without warning, which could lead to a loss of funds for miners (Quora). To mitigate these risks, miners should research and select reputable pools, monitor pool performance, and diversify across multiple pools when possible.
Cost Considerations
Mining Ethereum requires a substantial initial investment and ongoing costs:
- Hardware Costs: The cost of purchasing or upgrading to a mining rig capable of handling Ethereum mining can be significant.
- Electricity Costs: Ethereum mining is energy-intensive, and the cost of electricity can heavily influence profitability.
- Maintenance Costs: Mining equipment requires maintenance and may need repairs or replacements over time.
Prospective miners need to conduct a thorough cost analysis to ensure that the potential rewards justify the expenses. It’s also advisable to stay informed about Ethereum’s upcoming transition to Proof of Stake, which may affect the long-term viability of mining.
Security Concerns
Securing mining operations and protecting against unauthorized mining are paramount:
- Malware and Phishing: Attackers may use phishing techniques to install mining malware on computers or infect websites to mine cryptocurrencies without the owner’s consent, leading to performance issues (Safe Computing – University of Michigan).
- Data Protection: Mining using improperly secured resources can put personal and institutional data at risk.
- Device Security: To prevent unauthorized mining, individuals should keep their software updated, avoid suspicious links, and be cautious with email attachments and shared documents (Safe Computing – University of Michigan).
Miners should employ robust security measures, such as using secure and updated mining software (monero-mining-software), protecting their devices, and being vigilant about potential security threats. Additionally, reporting any suspicious activities or security incidents related to mining is crucial for safeguarding one’s investments and the broader network.
Future of Ethereum Mining
The landscape of Ethereum mining is poised for significant changes as the network evolves. Key developments, including the transition to Proof of Stake (PoS), will have profound impacts on miners and the mining ecosystem.
Transition to Proof of Stake
In September 2022, Ethereum completed its transition to a Proof of Stake (PoS) model, moving away from the energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) system (Investopedia). This shift is aimed at making the network more secure, sustainable, and scalable. Unlike PoW, PoS does not require miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks. Instead, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
During this transition, Ethereum developers planned to implement a hybrid system before fully transitioning to PoS, allowing miners to gradually adapt to the changes (CoinCentral). This has reshaped the reward system for Ethereum miners and addressed the centralization concerns within the network.
Impact on Miners
The move to PoS has fundamentally changed the Ethereum mining landscape, affecting the profitability and role of miners. To become an independent validator on the Ethereum network, one must stake at least 32 ETH, which is a considerable investment. This high entry barrier has led many miners to join Ethereum mining pools as an alternative to becoming independent validators, allowing them to participate without owning the full 32 ETH.
However, there are certain limitations to accessing the staked ETH, as withdrawals may only be possible after specific network upgrades are completed, potentially by the end of the year. For those considering whether to stake their Ethereum, it’s essential to weigh the potential risks and rewards (should I stake my ethereum).
Emerging Trends
As Ethereum mining undergoes these changes, new trends are emerging within the crypto mining sector. Miners are exploring alternative cryptocurrencies that still operate under PoW, such as Litecoin.
Moreover, the focus on sustainability is prompting miners and investors to consider the environmental impact of their activities, leading to a surge in interest in more eco-friendly blockchain projects and cryptocurrencies.
As the Ethereum network continues to evolve, so too will the strategies and technologies employed by those involved in its mining and validation processes. Staying informed on the latest developments is crucial for anyone invested in the future of Ethereum mining and the broader cryptocurrency space.